SUWON, REPUBLIC OF KOREA
Smart Rain City Suwon
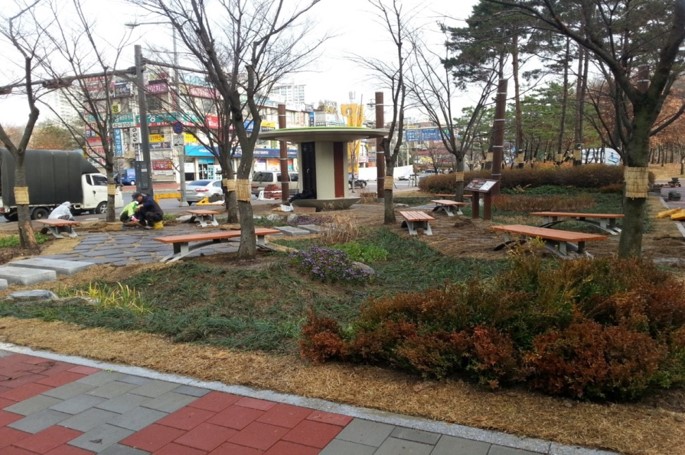

Suwon is the capital and largest city of Gyeonggi-do, South Korea's most populous province surrounding Seoul, with a population of 1.23 million. The extensive industrialisation and urbanisation of Suwon have brought several consequences: the increased impermeability of the land, reduced green and water catchment areas, increased risks of inundation, and water shortages. Under this circumstance, the city rolled out the Smart Rain City Suwon initiative to reverse this trend.
This initiative was an extension and evolution of the Rain City Suwon initiative and was implemented in four phases. The first phase focused on planning, including the Suwon Ordinance on Water Circulation Management and awareness-raising. The second and third phases witnessed the design and implementation of relevant policies and infrastructure, well informed by environmental big data analysis and resident opinions. These two phases ushered in various rainwater recycling and reuse facilities, e.g., permeable pavements, rainwater gardens, and roadside sprinkler systems. With the groundwork laid, the final phase of the initiative focused on the smart aspect of the initiative: to combine the rainwater management system with information and communications technologies, especially the Internet of Things, and realise integrated management of Suwon's smart city infrastructure.
The implementation of this initiative has brought about a 65% increase in rainwater permeation and a 49% decrease in surface runoffs, along with a large amount of water saved every year. Based on the smart rainwater facilities and data collected by the attached sensors, various solutions have also been developed to, for instance, reduce dust in the air and cool the city, contributing to improved air quality.
This initiative is of high relevance to SDGs 6 (clean water and sanitation), 9 (industry, innovation, and infrastructure), 11 (sustainable cities and communities), and 13 (climate action).


 In Focus | World Cities Day: People-Centred Smart Cities
In Focus | World Cities Day: People-Centred Smart Cities City Stories | Fostering community resilience: A lifeline for the Central African Republic
City Stories | Fostering community resilience: A lifeline for the Central African Republic In Focus | Innovative Education, Empowering Futures
In Focus | Innovative Education, Empowering Futures



















 Tel: +86 020 3780 4434
Tel: +86 020 3780 4434 Email: info@guangzhouaward.org
Email: info@guangzhouaward.org Address: Unit 01-7, 28th Floor, No. 7, Chunrong 3rd Road, Tianhe District, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510000, PRC
Address: Unit 01-7, 28th Floor, No. 7, Chunrong 3rd Road, Tianhe District, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510000, PRC




